 TOP
TOPRelated Products
Related Cases

Wet electric and wet dust removal project of Steel slag of Hebei Handan Zhongban Steel Mill

Shanxi Hongda steel slag wet electric Dust removal project

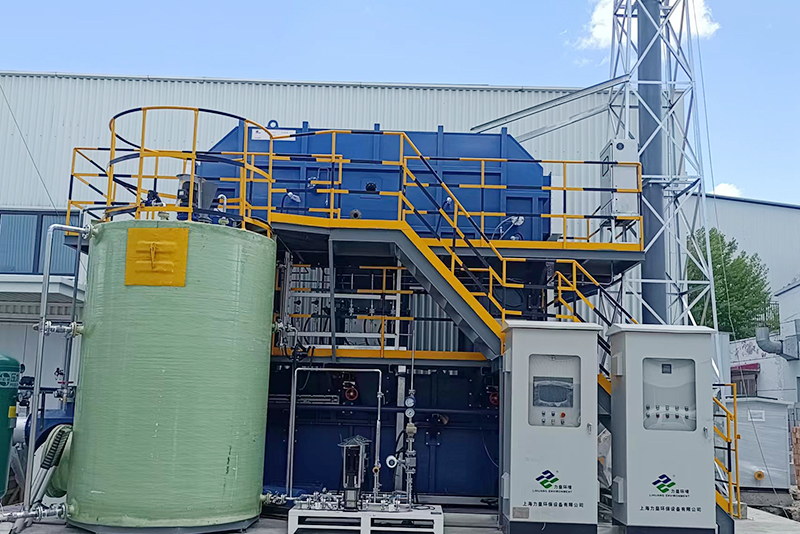
Shanghai Bulannuo Industrial packaging materials online monitoring project

China Tobacco Ningxia Hongde VOCs exhaust gas treatment project

Shanghai Hengjie Wood Industry VOCs waste gas treatment project

Pingyao Paper Mill desulfurization, denitration and dust removal EPC project
What is the difference between RTO and RCO?
RTO technology and RCO technology are VOCs (volatile organic compounds) treatment technology, is currently widely used, good treatment effect, stable operation, low cost of mature technology.
RTO refers to the Regenerative Thermal oxidizing technology. Its English name is Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer. RTO regenerative thermal oxidation heat recovery adopts a new unsteady heat transfer mode, the principle is to heat the organic waste gas to 760℃ above the VOC in the waste gas oxidation decomposition into CO2 and H2O. The high temperature gas generated by oxidation flows through the special ceramic heat storage body, which heats up the ceramic body and "accumulates heat". This heat storage is used to preheat the following organic waste gas, so as to save the fuel consumption of exhaust gas heating up. The decomposition efficiency of RTO is 95%-99%.
RCO refers to the Regenerative Catalytic Oxidation Oxidition. The principle of RCO regenerative catalytic combustion method is as follows: the first step is the adsorption of VOC molecules on the catalyst to improve the concentration of reactants; the second step is the catalytic oxidation stage to reduce the activation energy of the reaction and improve the reaction rate. With the help of catalyst, organic waste gas can occur anaerobic combustion at a lower ignition temperature and decompose into CO2 and H2O to release a lot of heat. Compared with direct combustion, it has the characteristics of low ignition temperature and small energy consumption. In some cases, it does not need external heating after reaching the ignition temperature, and the reaction temperature is 250-400℃.
