 TOP
TOPRelated Products
Related Cases

Wet electric and wet dust removal project of Steel slag of Hebei Handan Zhongban Steel Mill

Shanxi Hongda steel slag wet electric Dust removal project

Shanghai Bulannuo Industrial packaging materials online monitoring project

China Tobacco Ningxia Hongde VOCs exhaust gas treatment project

Shanghai Hengjie Wood Industry VOCs waste gas treatment project

Pingyao Paper Mill desulfurization, denitration and dust removal EPC project
Development history of regenerative combustion device RTO
Basic concepts of RTO
Regenerative combustion device, referred to as RTO, refers to the combustion and purification treatment of industrial organic waste gas, and the use of heat accumulator to treat the treatment of waste gas for heat exchange and heating, after purification of exhaust gas for heat exchange and cooling device. Combustion device for VOCs combustion temperature mainly depends on the most difficult oxide natural point. Most temperatures are required to be above 200-300℃, the point of ignition of the most difficult oxidized components, so the combustion temperature is usually designed to be between 760℃ and 850℃.
The history of RTO
The development of heat recovery methods and materials has been a key driver of RTO development.
As a combustion device, its energy consumption is one of the most noteworthy indicators, so the efficiency of heat recovery is crucial in the development of RTO. From the original direct fire combustion device, heat transfer oxidation device, and then heat storage oxidation device.
Heat exchanger oxidizer uses metal heat exchanger to realize heat energy recovery. Due to the low heat conduction coefficient between gas and metal interface parts of heat exchanger, the general heat recovery rate is about 65%, and the heat transfer efficiency is closely related to combustion temperature.
In order to pursue higher thermal efficiency, as early as the middle of the 19th century, Willian Siemens was studying the use of heat storage materials for thermal energy recovery. At that time, grid brick was used as heat storage body. Due to the large volume of regenerator, high cost, long reversing time and large temperature fluctuation of preheating gas, its heat recovery efficiency was not high. It was not until 1982 that British Company Hotwork Development and British Gas jointly developed a new regenerative ceramic burner using ceramic spheres as heat accumulators.
Using ceramic ball as heat storage material is a key milestone in the development of heat storage combustion device. At this time, the reversing time is greatly shortened from minute meter to second meter, which greatly improves the recovery capacity of waste heat and the level of air preheating, and has obvious energy-saving effect.
In the early 1990s, Japan NKK and Japan Industrial Furnace Company developed a combustion device integrating efficient heat recovery and low NOx combustion by using honeycomb ceramic body as heat storage material. Honeycomb ceramic is used as heat storage material, which is transformed on the basis of ceramic ball. Compared with the ceramic honeycomb heat storage material, it has the advantages of large specific surface area, large heat storage and release rate, large effective circulation area, and small resistance loss. Because of the combination of energy saving and environmental protection, the combustion technology using this regenerative burner is called the second generation regenerative combustion technology, also known as high temperature air combustion (HTAC) technology.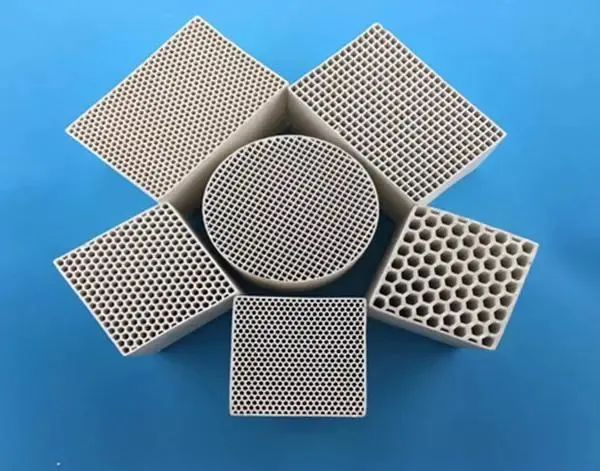
As a heat accumulator, honeycomb ceramics have changed the traditional regenerator greatly. From the original lattice brick to ceramic ball, and then to honeycomb ceramic body, the specific surface area of the regenerator increases sharply, the volume decreases significantly, the reversal time is greatly shortened, the heat exchange performance is greatly improved, and the pollutant discharge is far below the environmental protection standard. HTAC technology combined with it is also known as one of the key technologies of the 21st century.
In China, RTO technology emerged gradually after 2001. At the beginning of this century, the first set of domestic RTO was born in Lanzhou Ruima Tianhua Chemical Machinery and Automation Research Institute Ruima Company. Since then, domestic manufacturers have continuously assimilated and absorbed foreign advanced technology, and constantly changed and innovated in the process of engineering practice.
The type of RTO
The regenerative combustion device usually consists of reversing device, regenerative chamber, combustion chamber and control system. Rtos can be divided into tower type and rotary type according to the difference of their equipment structure.
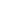
01 tower RTO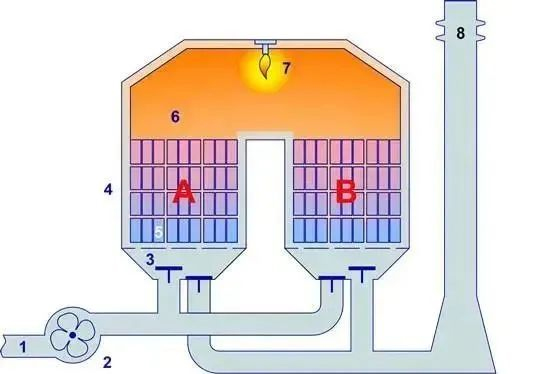
Tower RTOS include the first generation of two-compartment RTOS and multi-compartment Rtos. It is characterized by two or more ceramic filled regenerator chambers, through the switch of the valve, the regenerator preheating and heat recovery, so as to achieve the purpose of preheating. The two-tower RTO lacks a cleaning process. At the end of the cycle, some of the waste gas remains in the regenerator. When the valve is reversed, the untreated waste gas is discharged directly through the chimney. Therefore, the VOCs processing efficiency of two-tower RTO is lower than that of three-tower RTO. At present, the purpose of improving the efficiency of two-tower RTO is to cache the residual waste gas through the design of buffer tank, and then burn it again through reflux.
When the air volume of exhaust gas is too large, generally above 60000Nm3/H, tower rooms need to be added to ensure the heat transfer efficiency and wind equalization effect of air flow when tower RTO is adopted.
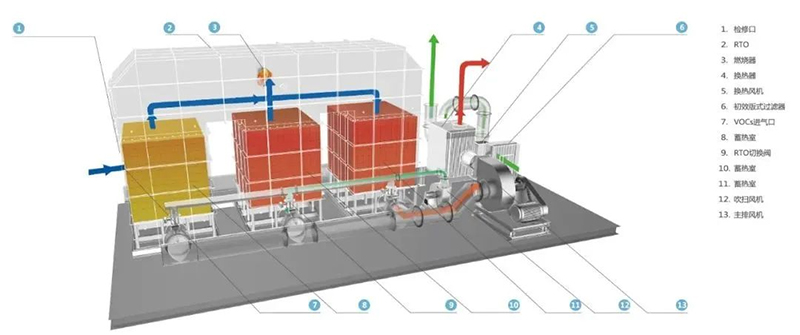
02 Rotary RTO
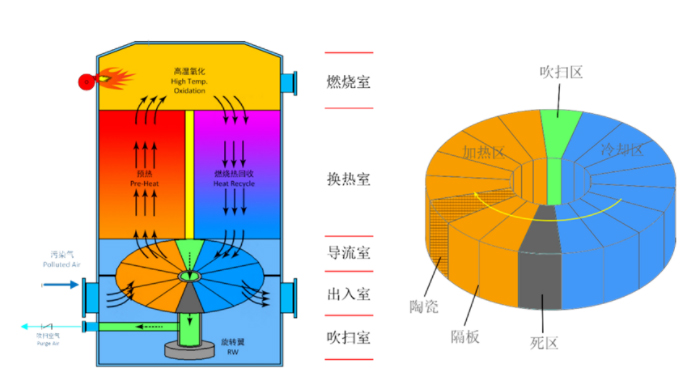
Rotary RTO appeared in the late 1990s and is the third generation of RTO development technology. The exhaust gas is sequentially guided into or out of a specific part of the combustion chamber through rotating valve (regenerative cylinder) rotation, indexing, exhaust gas distribution and other actions. The rotor is divided into inlet and outlet parts by a sealing device arranged on the surface of the rotor, through which the waste gas before treatment and the purified gas are respectively introduced into or discharged from the RTO combustion chamber. In the current development process of rotary RTO, there are different designs in the operation mode of rotary valve, purging mode, sealing mode and partition of regenerative chamber, so different types of RTO have been derived.
Regenerative combustion device (RTO), as an important technology in VOCs end treatment process, has been widely used in coating, packaging and printing, chemical industry and other industries. On the basis of the single combustion process, according to the working condition, the combination process, effectively realize the effective treatment of waste gas and energy conservation.
In the development process of RTO, we can see that the development of thermal storage materials is a strong push for the mature steps of RTO technology. RTO of different mechanical structures is an adaptive change to application scenarios, but also to improve processing efficiency, energy saving of operation and convenience of maintenance.